Queues
Call queues are used to distribute calls to the agents subscribed to the queue. Queues are managed
with the /queues endpoints
A queue can be configured with the following options:
A options: strategy defines how queue members are called when a call enters the queue. A queue can
use one of the following ring strategies:
linear: For each call, in the same order, starting from the same member- For agents: In login order
- For static members: In definition order
leastrecent: call the member who least recently hung up a callfewestcalls: call the member with the fewest completed callsrrmemory(round robin with memory): call the "next" member after the one who answered lastrandom: call a member at randomwrandom(weight random): same as random, but taking the member penalty into accountringall: call all members at the same time
Warning: When editing a queue, you can't change the ring strategy to linear. This is due to an asterisk limitation. Unfortunately, if you want to change the ring strategy of a queue to linear, you'll have to delete it first and then create a new queue with the right strategy.
Note: When an agent is a member of many queues the order of call distribution between multiple queues is non-deterministic and cannot be configured.
Timers
You may control how long a call will stay in a queue using different timers:
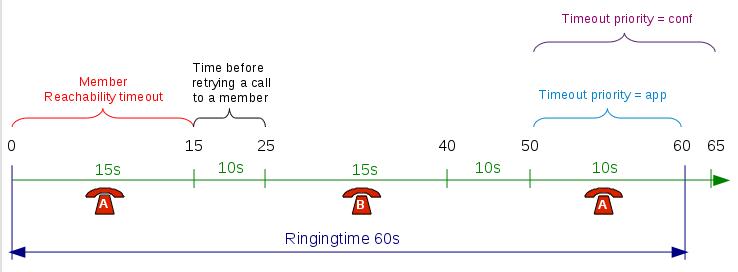
options: timeout(Member reachability time out): Maximum number of seconds a call will ring on an agent's phone. If a call is not answered within this time, the call will be forwarded to another agent.retry_on_timeout(Time before retrying a call to a member): Used once a call has reached the "Member reachability time out". The call will be put on hold for the number of seconds allowed before being redirected to another agent.timeout(Ringing time): The total time the call will stay in the queue.options: timeoutpriority(Timeout priority): Determines which timeout to use before ending a call. When set to "configuration", the call will use the "Member reachability time out". When set to "dialplan", the call will use the "Ringing time".
Fallbacks
Calls can be diverted on no answer with /queues/{queue_id}/fallbacks endpoints:
noanswer_destination: The call reached thetimeoutand no agent answered the call.congestion_destination: The number of calls waiting has reached theoptions: maxlen.fail_destination: No agent was available to answer the call when the call entered the queue (options: joinempty) or the call was queued and no agents were available to answer (options: leavewhenempty).
Diversions
Diversions can be used to redirect calls to another destination when a queue is very busy. Calls are
redirected using one of the two threshold: wait_ratio_threshold and ẁait_time_threshold
The diversion check is done only once per call, before the preprocess subroutine is executed and before the call enters the queue.
wait_time_threshold
When this scenario is used, the administrator can set a destination for calls to be sent to when the
estimated waiting time is over the threshold wait_time_threshold.
Note that if a new call arrives when there are no waiting calls in the queue, the call will always be allowed to enter the queue.
Note:
- this estimated waiting time is computed from the actual hold time of all answered calls in the queue (since last asterisk restart) according to an exponential smoothing formula
- the estimated waiting time of a queue is updated only when a queue member answers a call.
wait_ratio_threshold
When this scenario is used, the administrator can set a destination for calls to be sent to when the
number of waiting calls per logged-in agent is over the wait_ratio_threshold.
The number of waiting calls includes the call for which the check is currently being performed.
The number of logged-in agents is the sum of user members and currently logged-in agent members. An agent only needs to be logged in and a member of the queue to participate towards the count of logged-in agents, regardless of whether he is available, on call, on pause or on wrapup.
The maximum number of waiting calls per logged-in agent can have a fractional part.
Here are a few examples:
wait_ratio_threshold: 1
Current number of waiting calls: 2
Current number of logged-in agents: 2
Number of waiting calls per logged-in agent when a new call arrives: 3 / 2 = 1.5
Call will be redirected to ``wait_ratio_destination``
wait_ratio_threshold: 0.5
Number of waiting calls: 5
Number of logged-in agents: 12
Number of waiting calls per logged-in agent when a new call arrives: 6 / 12 = 0.5
Call will not be redirected to ``wait_ratio_destination``
Note that if a new call arrives when there are no waiting calls in the queue, the call will always be allowed to enter the queue. For example, in the following scenario:
wait_ratio_threshold: 0.5
Current number of waiting calls: 0
Current number of logged-in agents: 1
Number of waiting calls per logged-in agent when a new call arrives: 1 / 1 = 1
Even if wait_ratio_time (1) is greater than the maximum (0.5), the call will still be accepted
since there are currently no waiting calls.
Music on Hold
The music_on_hold of the queue will be played:
- When the caller is waiting to be answered.
- When the caller is put on hold by an agent who already answered.
If you want a different music to be played when the caller is put on hold after being answered, you need to make some more configuration:
-
Write an AGI script that will set the channel variable
CHANNEL(musicclass)to the name of the music-on-hold class you want the caller to hear when he is put on hold by the agent. Save this script to e.g./usr/local/bin/agi-agent-hold-moh. -
Add the following preprocess subroutine on the queue:
[setup-agent-hold-moh]
exten = s,1,NoOp(Setting AGI script for custom agent hold music)
same = n,Set(XIVO_QUEUEAGI=/usr/local/bin/agi-agent-hold-moh)
same = n,Return
This configuration will give the following scenario:
- The caller calls the queue
- The caller hears the music on hold of the queue
- The agent answers the call
- Wazo calls the AGI script, setting the new music on hold
- The caller and the agent talk together
- The agent puts the caller on hold
- The caller hears the new music on hold, set by the AGI script